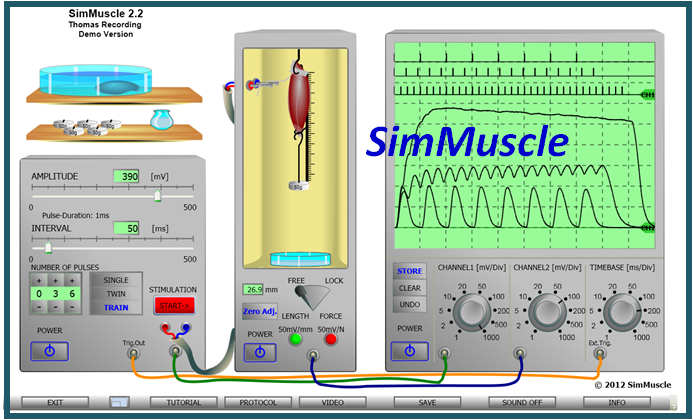
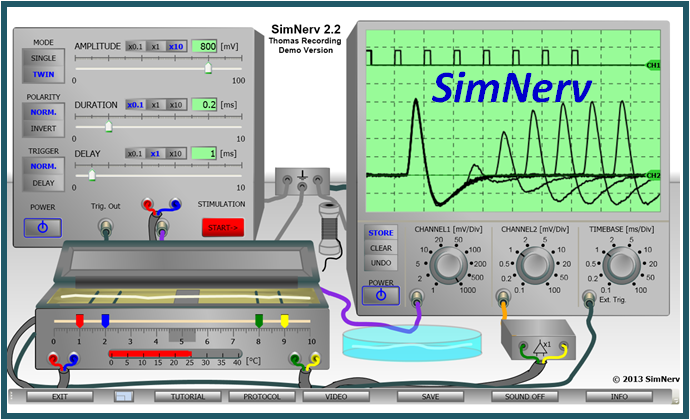
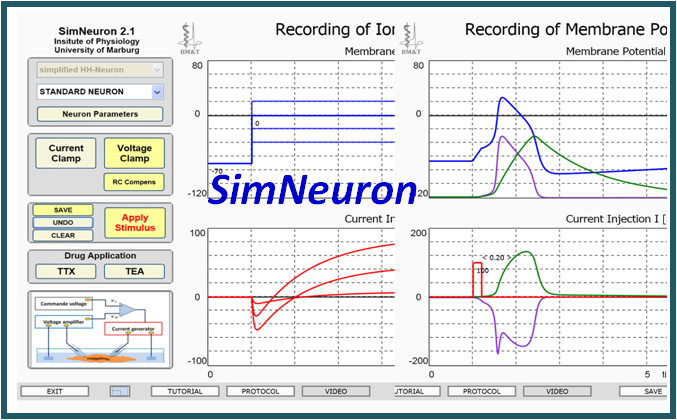
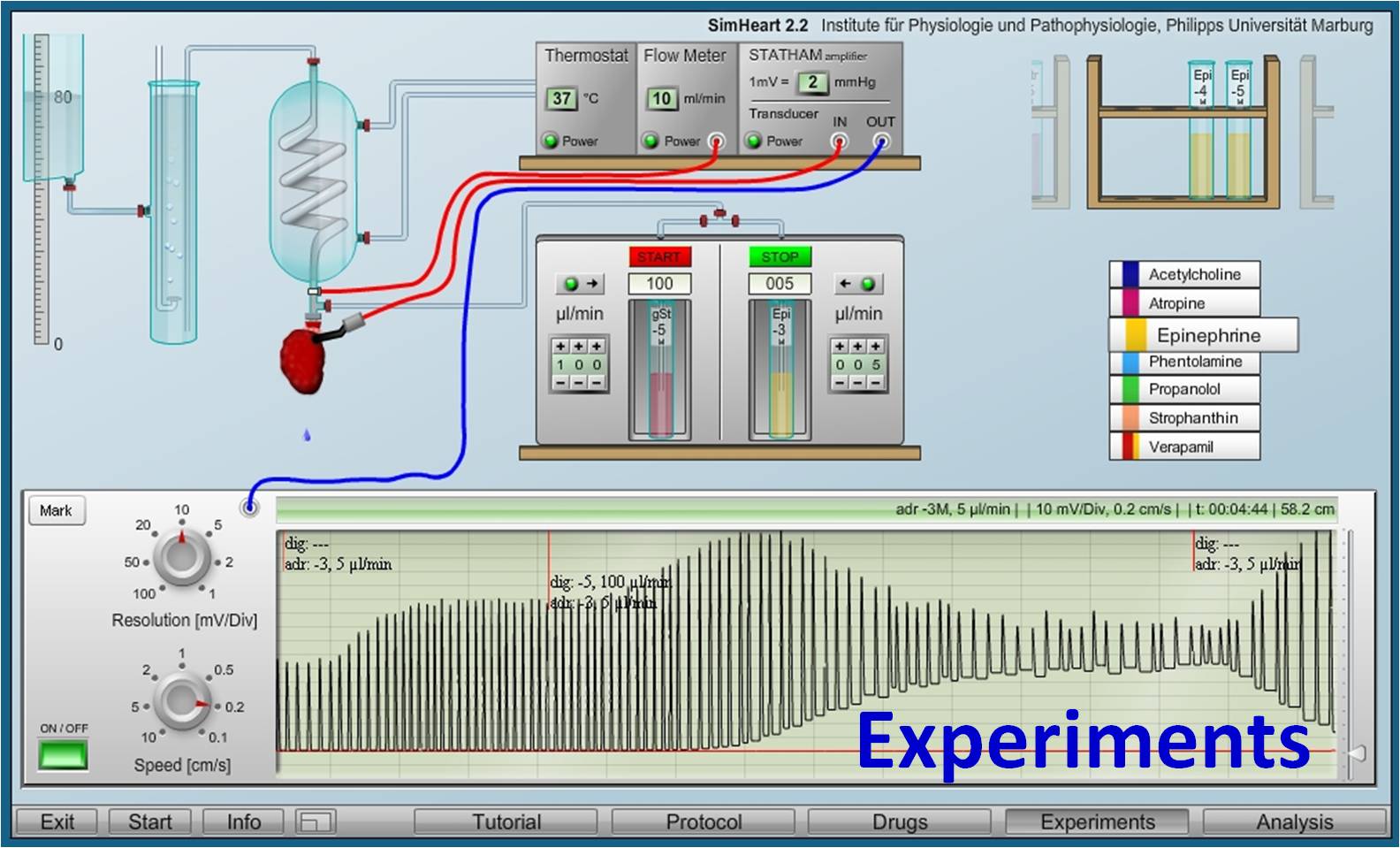
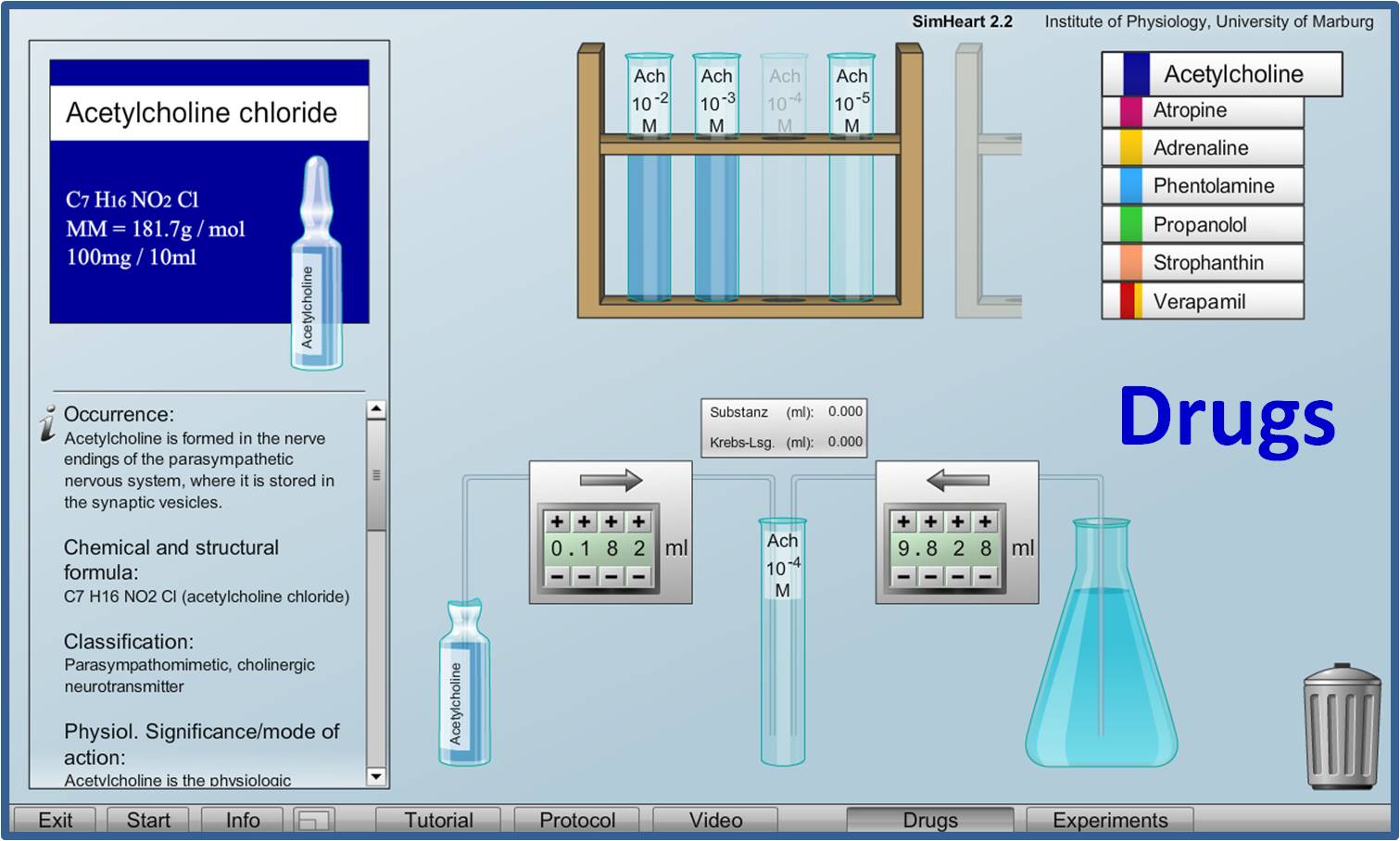
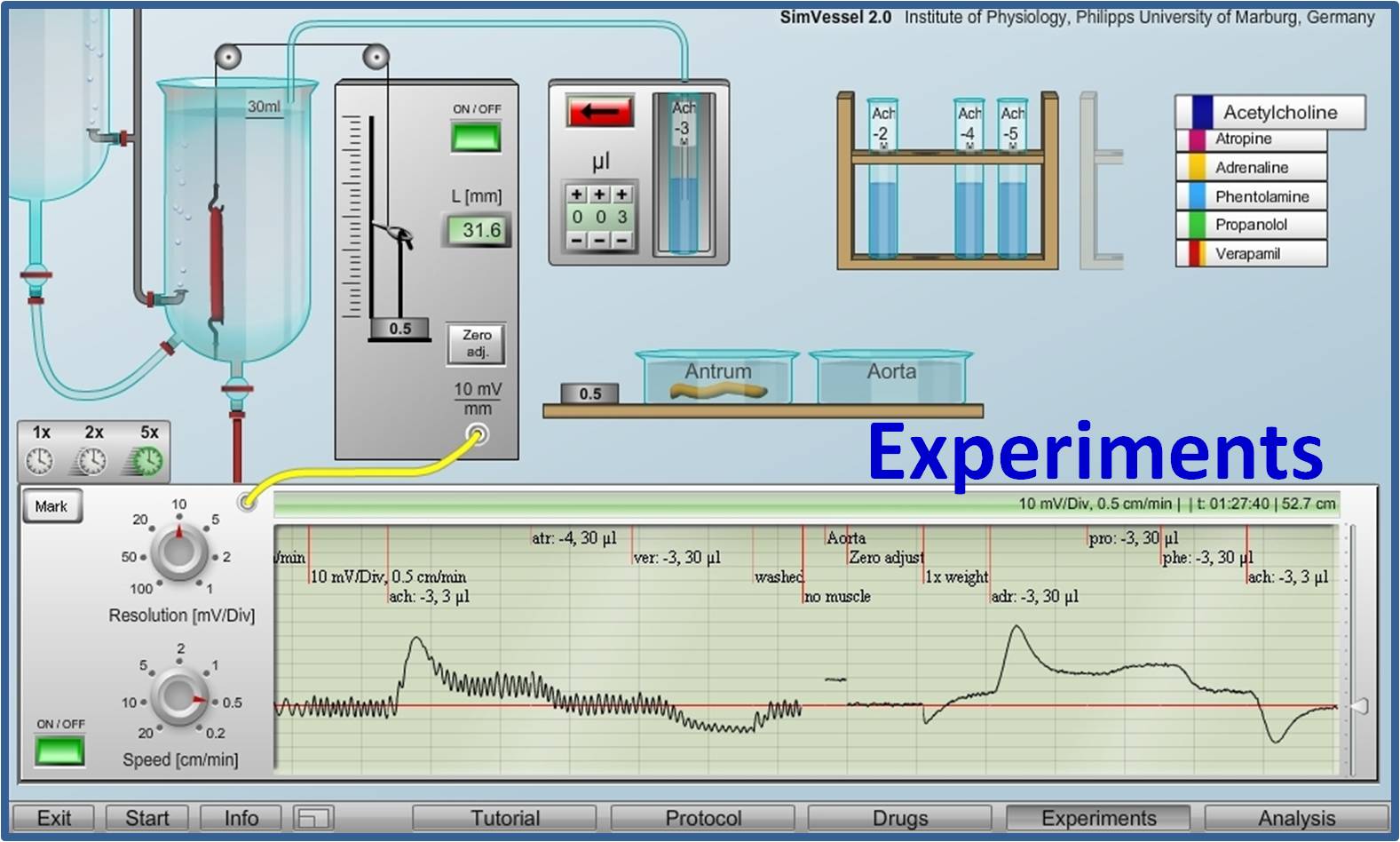
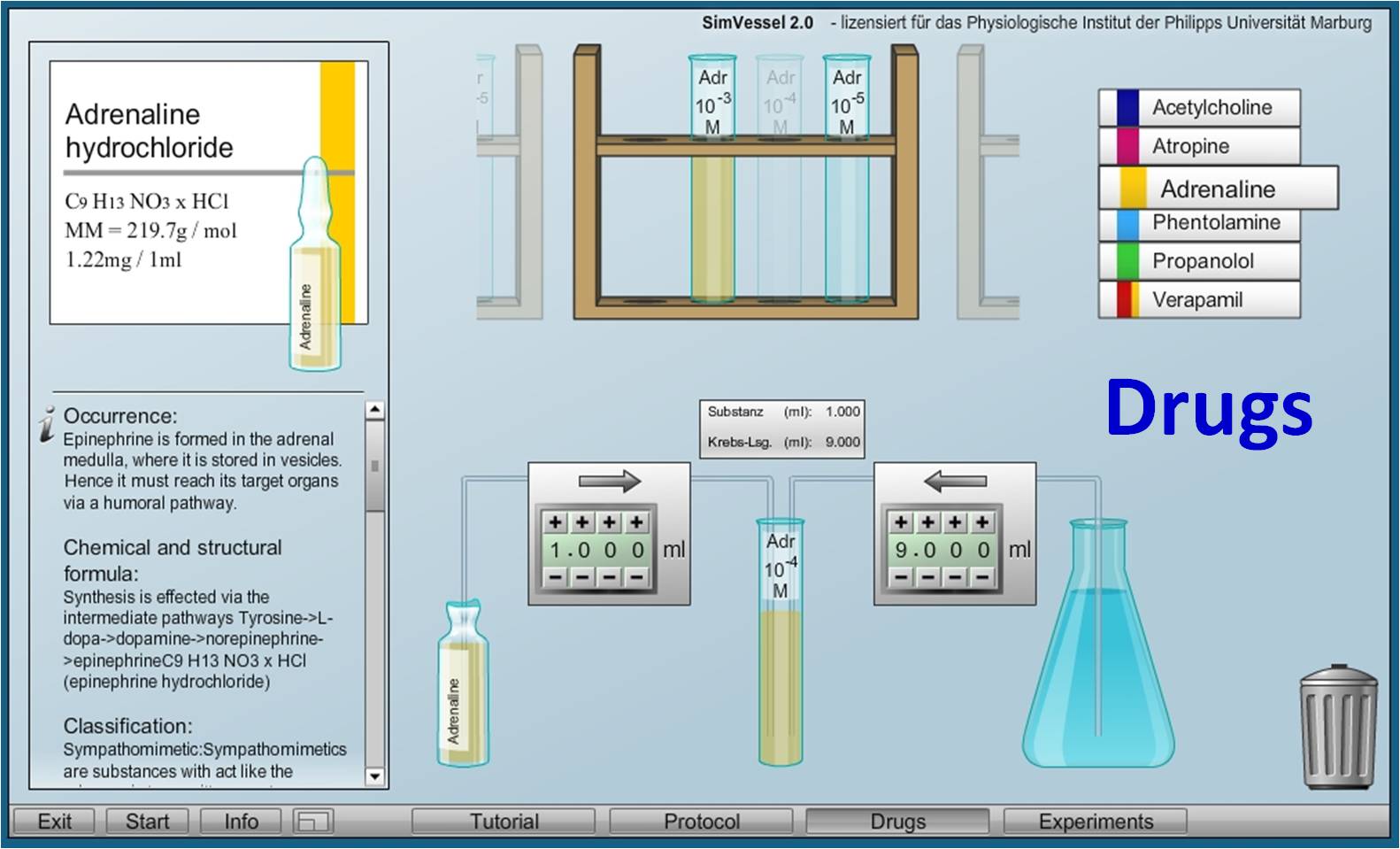
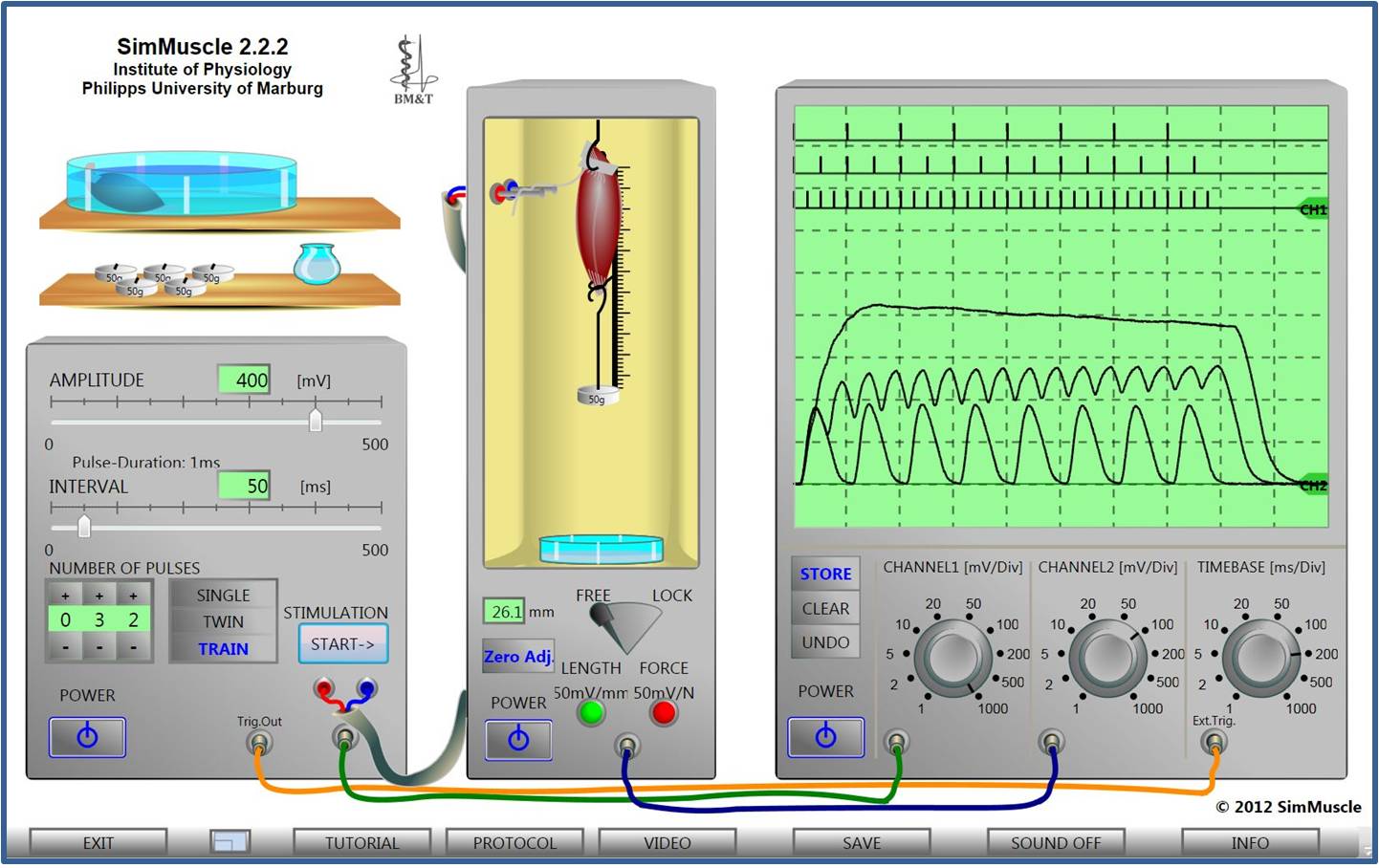
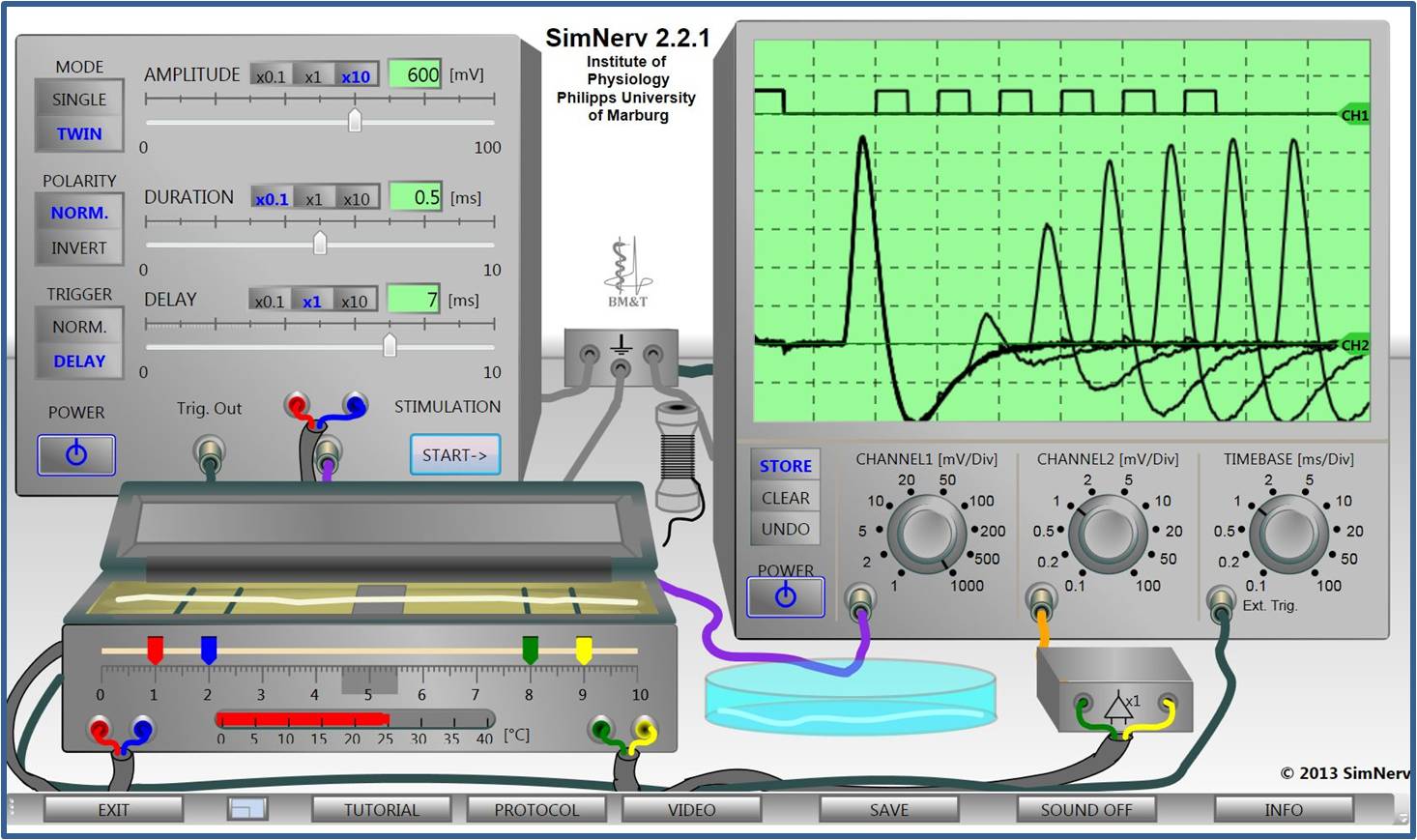
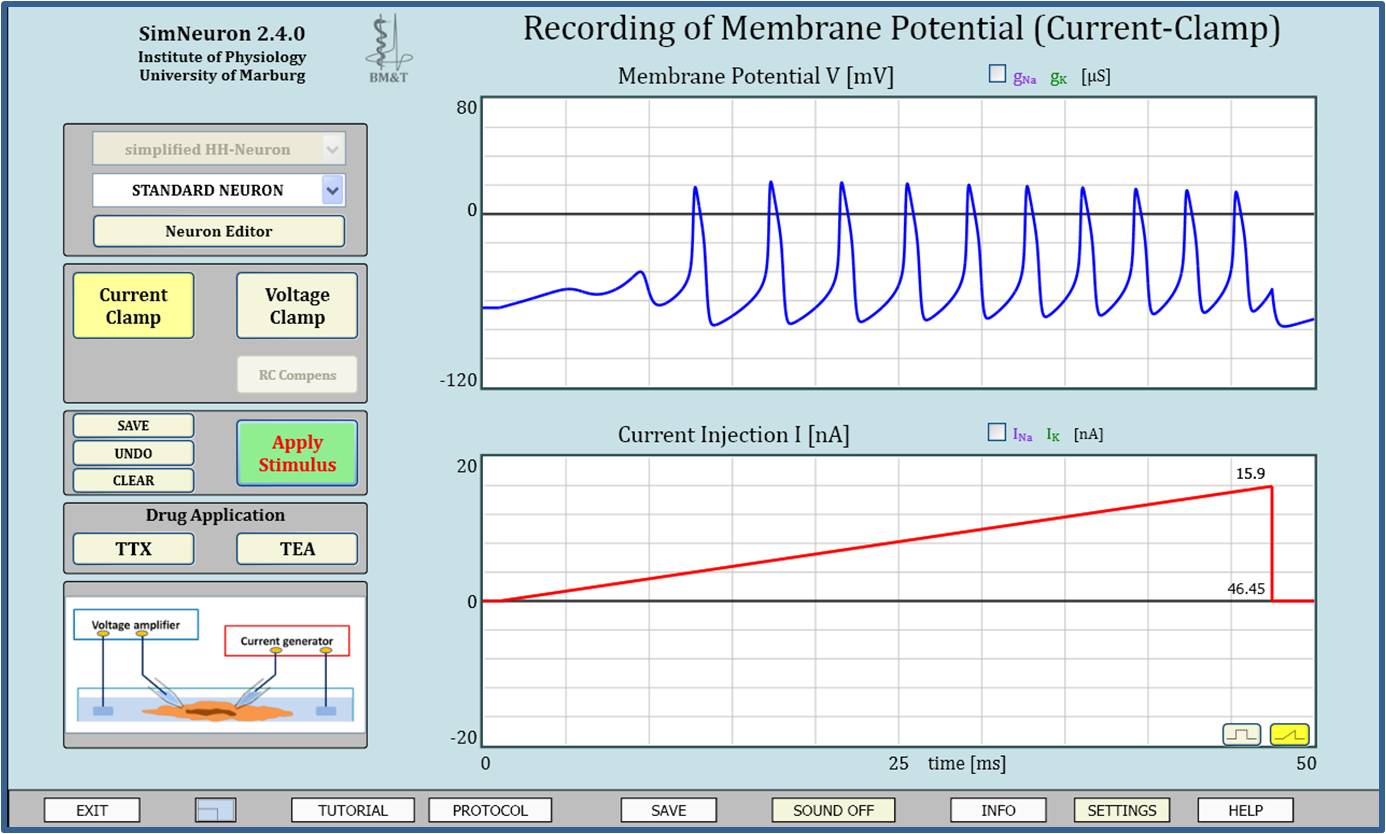
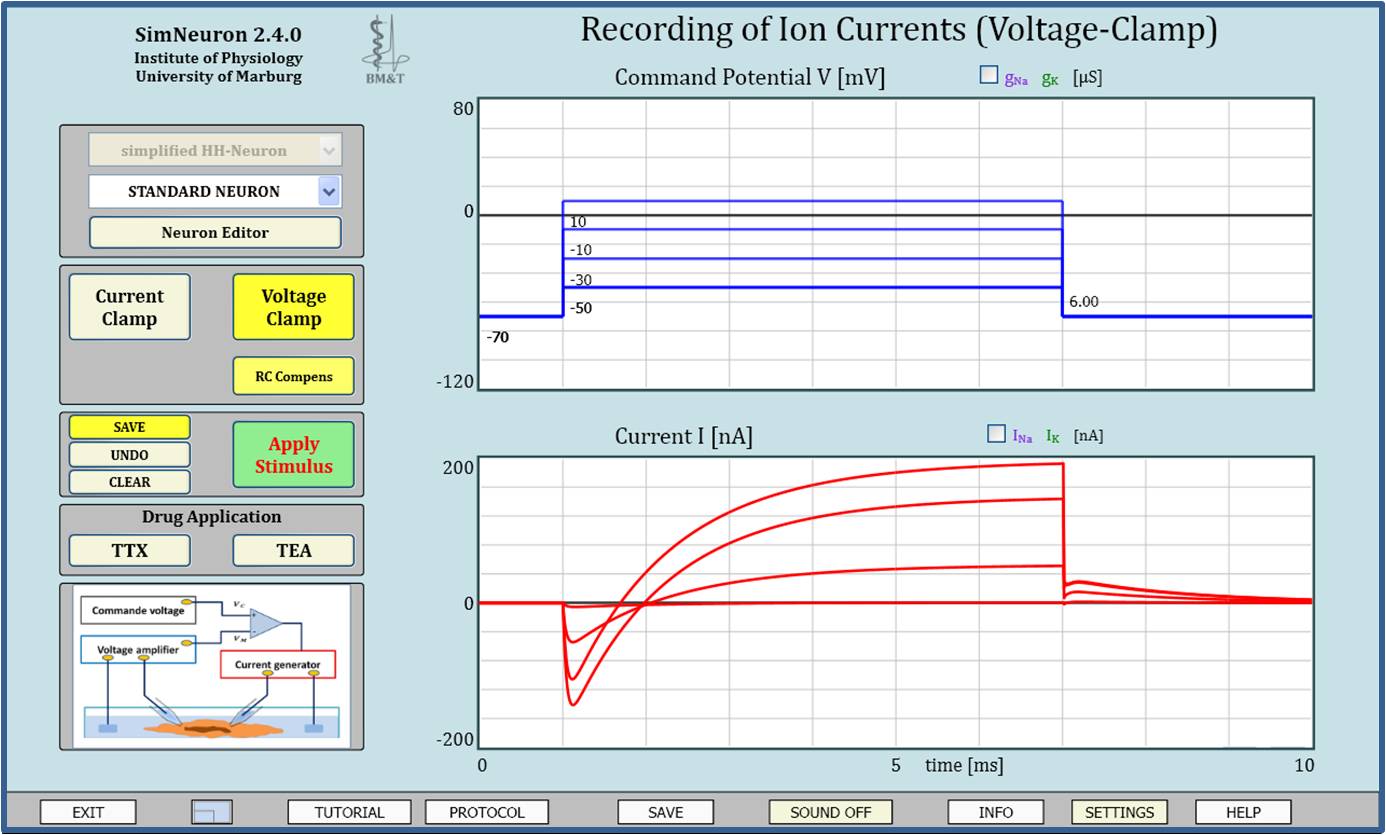
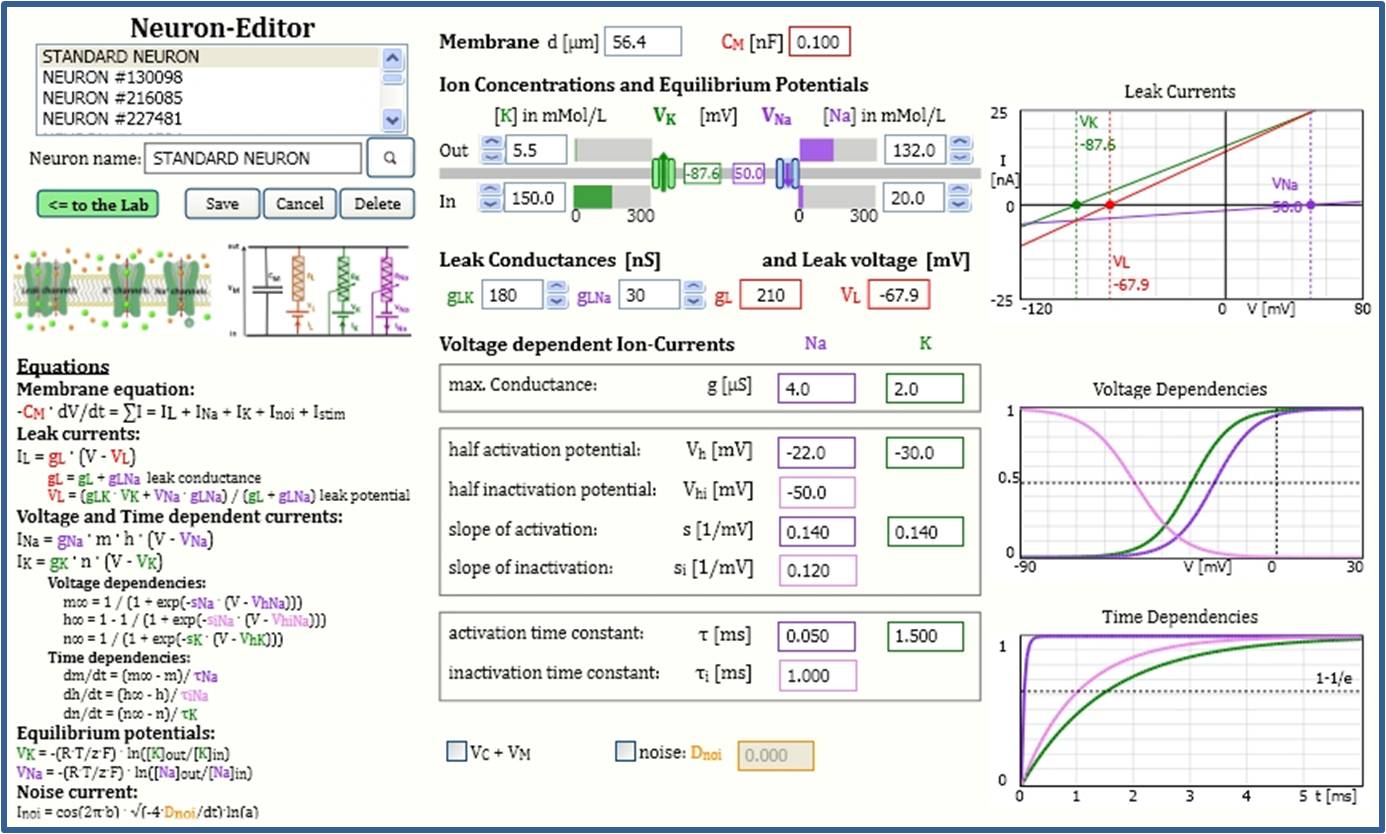
Virtual Physiology
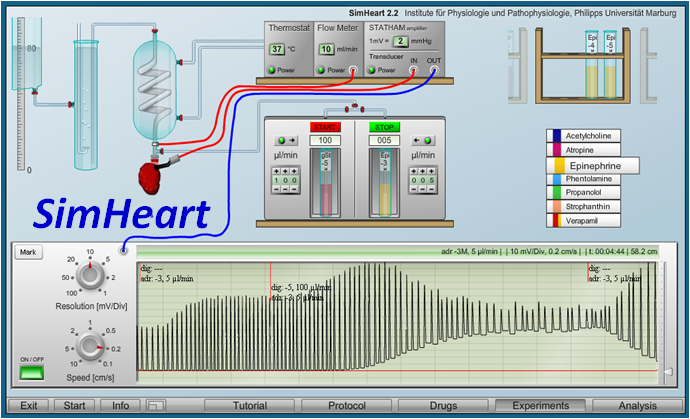
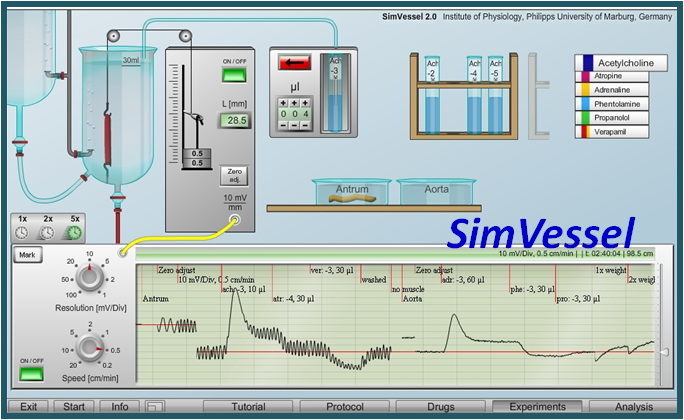
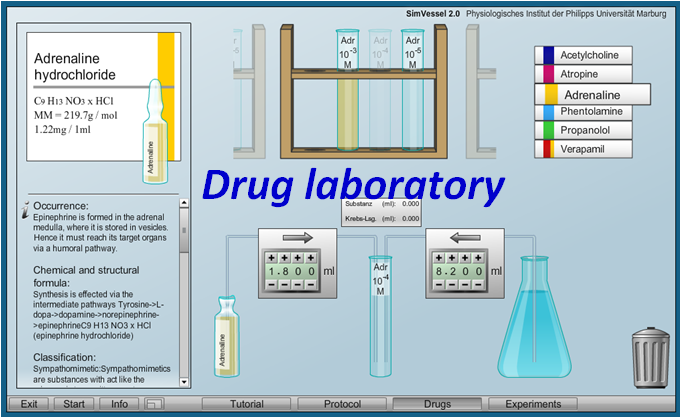
the unique truly simulation software
physiology and pharmacology experiments
in virtual laboratories
almost like in the real world
- Perfect for online teaching and remote learning -